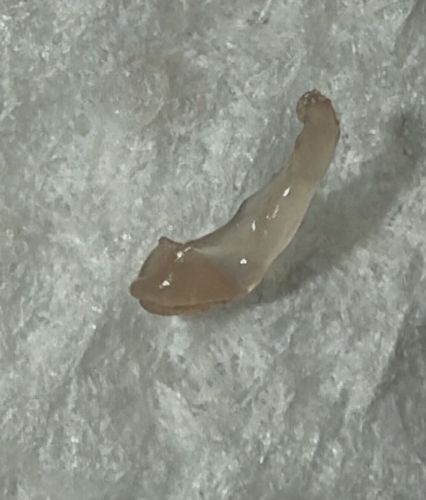
Slug
Scientific Name: Gastropoda (Class level, specific species difficult without location)
Order & Family: Order: Stylommatophora; Family: Various (e.g., Limacidae, Agriolimacidae)
Size: Varies greatly by species; from less than 1 cm (0.4 inches) to over 15 cm (6 inches). The specimen shown appears to be a small juvenile or a small species.
Natural Habitat
Found in moist environments, often in gardens, under rocks, logs, or leaf litter. They thrive in damp, improved soils and are nocturnal foragers.
Diet & Feeding
Herbivorous and detritivorous; they feed on living plants (leaves, stems, fruits), decaying plant matter, fungi, and sometimes carrion.
Behavior Patterns
Slugs move by gliding on a muscular foot lubricated by mucus (slime). They are hermaphroditic (possess both male and female reproductive organs). They are primarily active at night or on rainy days to avoid dehydration.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Can be significant agricultural and garden pests, eating holes in leaves and fruit. They can transmit parasites like lungworm to pets if ingested. Benefits: They play a crucial role in decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the soil.
Identified on: 2/12/2026