Booklouse
Scientific Name: Liposcelis spp.
Order & Family: Psocoptera, Liposcelididae
Size: 1-2 mm
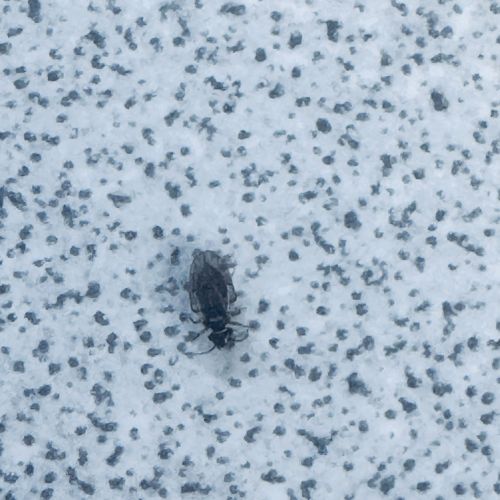
Natural Habitat
Damp, warm, and dark environments; often found in books, stored food products, wallpaper, and other paper products, as well as in undisturbed areas indoors.
Diet & Feeding
Fungi, mold, starch, glue in bookbindings, paste, flour, and other organic matter.
Behavior Patterns
Booklice are non-biting and non-stinging insects that thrive in high humidity. They are often active in undisturbed settings and can rapidly reproduce under favorable conditions. They are not known to transmit diseases to humans or animals.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include damage to books, paper products, and stored food items due to feeding on mold and starches. They are considered a nuisance pest in homes. No significant benefits are known in a human-centric context, though they contribute to the decomposition of organic matter in natural environments.
Identified on: 11/20/2025