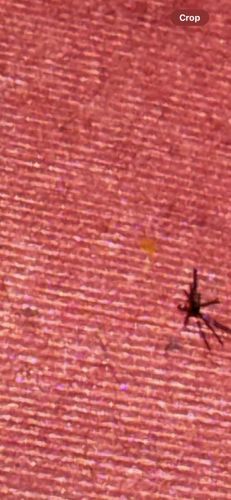
Cellar Spider (or Daddy Long-legs Spider)
Scientific Name: Pholcus phalangioides
Order & Family: Order: Araneae, Family: Pholcidae
Size: Body length typically 2-10 mm, with very long, thin legs that can span up to 50 mm.
Natural Habitat
Commonly found in dark, damp, and undisturbed areas such as cellars, basements, crawl spaces, attics, garages, and sheds. They also occur outdoors in similar sheltered locations.
Diet & Feeding
Cellar spiders are predatory and feed on a variety of other insects and spiders. They are known to even prey on more venomous spiders like Black Widows. They capture prey within their webs.
Behavior Patterns
Cellar spiders are known for their rapid, vibrating movement when disturbed, which makes them difficult for predators to catch. They are largely nocturnal and build irregular, messy webs in corners and other undisturbed areas. Females lay eggs in a silk sac and carry them in their fangs until they hatch. They are not aggressive towards humans.
Risks & Benefits
Cellar spiders are generally harmless to humans. Their bites are rare and, if they occur, are not considered medically significant. They are beneficial as natural pest control, preying on other insects and spiders in homes.
Identified on: 8/30/2025