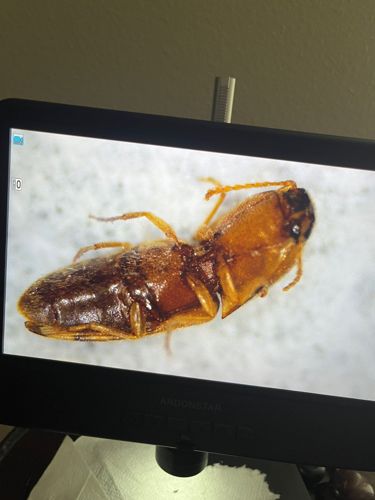
Click Beetle
Scientific Name: Elateridae
Order & Family: Coleoptera (Beetles), Elateridae (Click Beetles)
Size: Typically 3-30 mm, though some species can be larger.
Natural Habitat
Widely diverse habitats including forests, grasslands, agricultural fields, gardens indoors and outdoors. Larvae (wireworms) live in soil.
Diet & Feeding
Larvae (wireworms) are primarily herbivorous, feeding on roots, seeds, and tubers of various plants, including crops. Some larvae are predatory on other insects. Adult click beetles often feed on nectar, pollen, tender leaves, or are not known to feed at all.
Behavior Patterns
Adult click beetles are known for their unique 'clicking' mechanism; when overturned, they can arch their body and snap a spine on their prosternum into a groove on their mesosternum, creating an audible click and launching themselves into the air to right themselves. Larvae (wireworms) are often found underground and can be quite destructive to crops. They have a relatively long larval stage, sometimes lasting several years.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Wireworms (larvae) can be significant agricultural pests, causing damage to root crops (e.g., potatoes, corn, wheat) leading to substantial economic losses. Benefits: Some species (both larval and adult) are predatory on other insect pests, thus contributing to biological control. They are also part of the broader ecosystem as a food source for birds and other animals.
Identified on: 9/5/2025