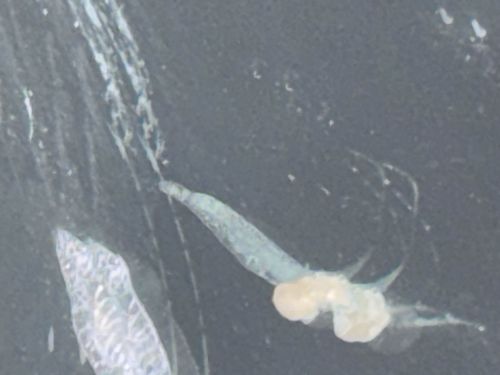
Anchor Worm
Scientific Name: Lernaea cyprinacea
Order & Family: Order Cyclopoida, Family Lernaeidae
Size: 8 mm to 22 mm for adult females; males are microscopic.
Natural Habitat
Freshwater environments such as ponds, lakes, and aquariums, attached to the skin, fins, or gills of fish hosts.
Diet & Feeding
Parasitic; females use specialized mouthparts to burrow into the host fish's flesh to feed on blood and tissue fluids.
Behavior Patterns
Adult females are permanent ectoparasites that lose most of their crustacean features. They undergo multiple larval stages (nauplius and copepodid) before mating. After mating, the female burrows into a fish host, while the male dies.
Risks & Benefits
Pathogenic to freshwater fish; causes inflammation, secondary bacterial or fungal infections, and can lead to host mortality. They offer no known benefits to the ecosystem and are considered a major pest in aquaculture.
Identified on: 1/3/2026