Scabies Mite (Burrow)
Scientific Name: Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis
Order & Family: Order: Sarcoptiformes, Family: Sarcoptidae
Size: Microscopic; adult females are 0.30–0.45 mm long, while males are smaller. The visible burrow/rash is usually a few millimeters to over a centimeter long.
Natural Habitat
The mite is an obligate parasite that lives solely within the epidermis (upper layer) of human skin.
Diet & Feeding
Feeds on dissolved human tissue, typically not sucking blood but rather consuming skin cells and lymph.
Behavior Patterns
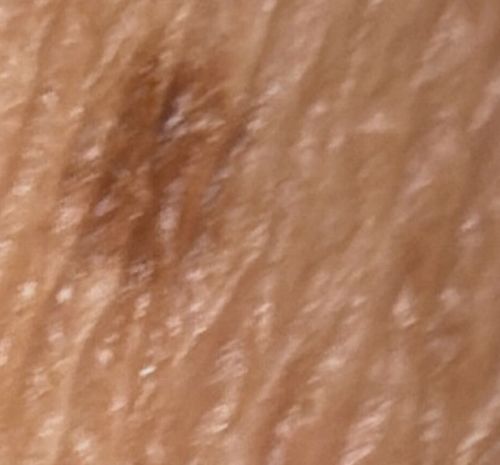
The female mite burrows into the stratum corneum of the skin to lay eggs, creating the characteristic grayish/brownish serpentine line seen in the image. They are most active and itchy at night.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Causes scabies, an intense itchy skin infestation that is highly contagious through direct skin-to-skin contact. Scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections like impetigo. Benefits: None.
Identified on: 2/18/2026