Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera / Cimicidae
Size: Adult bed bugs are typically 4-5 mm (0.16-0.20 inches) in length, similar to an apple seed. Nymphs (young bed bugs) are smaller.
Natural Habitat
Bed bugs are found worldwide. They typically inhabit human dwellings, especially bedrooms, living in mattresses, bed frames, headboards, cracks in walls, furniture, and even electrical outlets. They are adept at hiding in small spaces close to where their hosts rest.
Diet & Feeding
Bed bugs are obligate hematophagous insects, meaning they feed exclusively on blood. They prefer human blood but will also feed on other mammals and birds if humans are not available.
Behavior Patterns
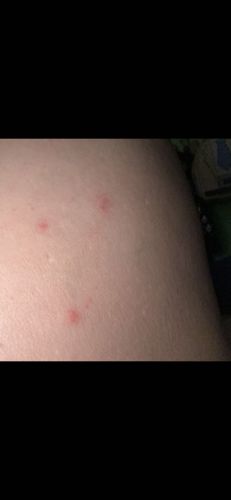
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal, feeding on humans (or other warm-blooded hosts) while they sleep. They are attracted to body heat and carbon dioxide exhaled by hosts. They often feed in a line or cluster, which can lead to multiple bites in a small area. They hide in cracks and crevices during the day, such as mattress seams, bed frames, furniture, and walls, and can be difficult to locate.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include itchy red welts (the bites), which can lead to secondary skin infections from scratching. In rare cases, severe infestations can cause iron deficiency anemia. They do not transmit diseases to humans. There are no known benefits to humans or the ecosystem, as they are considered pests.
Identified on: 9/4/2025