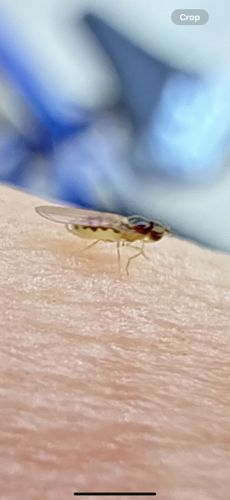
Fruit Fly
Scientific Name: Drosophila melanogaster (most common identification based on visual characteristics, though other species exist)
Order & Family: Order: Diptera, Family: Drosophilidae
Size: Typically 2-4 mm (0.08-0.16 inches) in length.
Natural Habitat
Commonly found near ripening or fermenting fruits and vegetables, kitchens, waste bins, and anywhere organic material is decaying or fermenting.
Diet & Feeding
Feeds on yeast, bacteria, and other microorganisms that grow on fermenting substances, particularly fruits and vegetables. They are attracted to the acetic acid produced during fermentation.
Behavior Patterns
Fruit flies have a short life cycle (about 7-14 days) and reproduce rapidly. Females lay hundreds of eggs on fermenting organic matter. They are quick to locate food sources and are often seen flying in small swarms around these areas.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Can be a nuisance pest in homes and commercial establishments dealing with food. While generally not harmful to humans, they can contaminate food with bacteria and other pathogens from their breeding sites. Benefits: Drosophila melanogaster is a very important model organism in biological research, particularly in genetics, due to its short life cycle, ease of breeding, and well-mapped genome. In nature, they play a minor role in decomposition.
Identified on: 10/17/2025