Mosquito
Scientific Name: Culicidae (various genera and species)
Order & Family: Diptera (Order), Culicidae (Family)
Size: Typically 3-6 mm (0.12-0.24 inches) in length, though some species can be larger.
Natural Habitat
Mosquitoes are typically found near standing water, which is essential for laying eggs and larval development. This includes ponds, marshes, swamps, puddles, clogged gutters, tree holes, and artificial containers holding water. Adults are often found in vegetated areas nearby.
Diet & Feeding
Female mosquitoes feed on blood to obtain protein for egg production, biting humans and other animals. Both male and female mosquitoes feed on nectar and plant juices for energy.
Behavior Patterns
Mosquitoes are most active during dawn and dusk, though some species bite throughout the day or night. They are attracted to carbon dioxide, body heat, and certain chemicals present on skin. After a blood meal, females seek out still water to lay their eggs, which can hatch into larvae that develop into pupae and then adult mosquitoes. They are known for their annoying buzzing sound.
Risks & Benefits
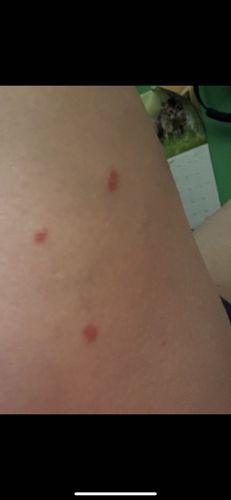
Potential risks include transmitting various diseases such as Malaria, Dengue Fever, West Nile Virus, Zika Virus, Chikungunya, and Yellow Fever, causing significant public health concerns. Their bites can also cause itchy, irritating welts. Benefits are less direct but include serving as a food source for other animals (e.g., bats, birds, fish) and playing a minor role in pollination.
Identified on: 9/6/2025