Human Itch Mite
Scientific Name: Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis
Order & Family: Order: Sarcoptiformes, Family: Sarcoptidae
Size: 0.3 to 0.45 millimeters in length
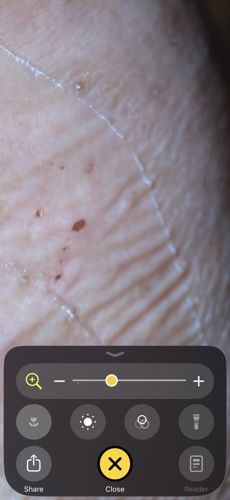
Natural Habitat
Extracellular environment within the human epidermis (skin)
Diet & Feeding
The mite feeds on human skin cells and extracellular fluid by burrowing into the stratum corneum
Behavior Patterns
Female mites burrow into the upper layer of the skin to lay 2-3 eggs per day. They are microscopic and typically spread through direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact.
Risks & Benefits
Causes scabies, a contagious skin infestation characterized by intense itching and pimple-like rashes. Risks include secondary bacterial infections from scratching. No ecosystem benefits as they are obligate parasites.
Identified on: 1/11/2026