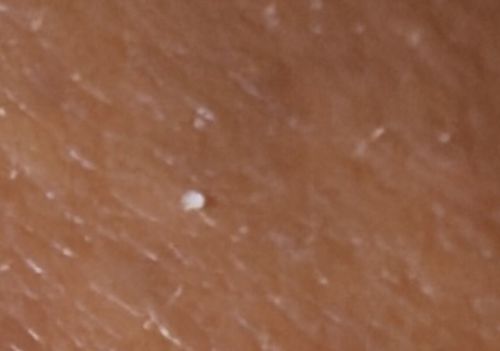
Pubic Louse Nit (Egg) or Head Louse Nit
Scientific Name: Pthirus pubis (ovum) or Pediculus humanus capitis (ovum)
Order & Family: Order: Phthiraptera, Family: Pthiridae (Pubic) or Pediculidae (Head)
Size: Approximately 0.3mm to 0.8mm in length (barely visible to the naked eye).
Natural Habitat
Found exclusively on human hosts, attached to hair shafts near the skin. Pubic lice prefer coarser hair in the genital region, chest, or armpits, while head lice frequent the scalp.
Diet & Feeding
The adult insects feed on human blood; the egg (nit) itself is a developing embryo and does not feed until it hatches.
Behavior Patterns
Nits are cemented firmly to hair shafts by female lice. They remain stationary until hatching (about 6-10 days). Identification often depends on whether they can be flicked off (dandruff/debris) or are stuck fast (nits).
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Infestations cause intense itching (pruritus) and potential secondary skin infections from scratching. They are highly contagious through close physical contact or shared items. Benefits: None known; they are obligate parasites.
Identified on: 2/11/2026