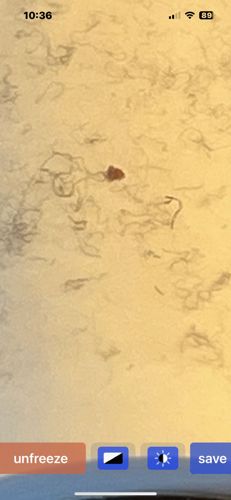
Nematodes (likely free-living or plant-parasitic, given appearance)
Scientific Name: Not identifiable to species or genus from the image. "Nematoda" is a phylum covering a vast range of species.
Order & Family: Order: Nematoda (Phylum)
Size: Most are microscopic, ranging from less than 0.1 mm to several millimeters in length. Some parasitic species can be much larger, up to several feet in length.
Natural Habitat
Extremely diverse, found in almost every habitat from polar regions to tropical zones. Abundant in soils, freshwater, marine environments, and as parasites within plants and animals.
Diet & Feeding
Free-living nematodes feed on bacteria, fungi, algae, and other microscopic organisms in soil and water. Plant-parasitic nematodes feed on plant roots and other tissues. Animal-parasitic nematodes feed on the tissues, blood, or intestinal contents of their hosts.
Behavior Patterns
Nematodes move using undulating motions. They can be free-living, parasitic on plants, or parasitic on animals. Their life cycles vary greatly depending on whether they are free-living or parasitic. Many soil nematodes play a role in nutrient cycling, while parasitic ones can cause significant damage to crops or health issues in hosts.
Risks & Benefits
Benefits: Many free-living nematodes contribute to soil health and nutrient cycling. Risks: Certain species are significant agricultural pests (e.g., root-knot nematodes), causing crop damage and yield loss. Others are human and animal parasites (e.g., pinworms, hookworms) causing various diseases.
Identified on: 8/27/2025