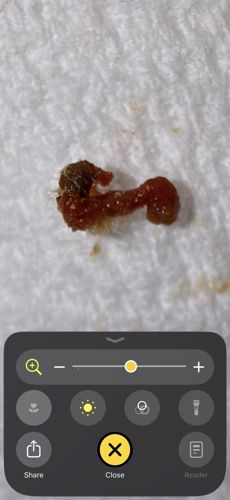
Bloodworm (Midge Larva)
Scientific Name: Chironomus species
Order & Family: Order: Diptera, Family: Chironomidae
Size: Generally 10mm to 25mm in length.
Natural Habitat
Stagnant or slow-moving freshwater bodies, often buried in soft sediment or mud at the bottom.
Diet & Feeding
They feed on organic debris, algae, and microorganisms found in the sediment. They are important decomposers in aquatic ecosystems.
Behavior Patterns
The larva builds protective tubes from silk and sediment. The reddish color comes from hemoglobin, which allows them to survive in low-oxygen environments. They eventually pupate and emerge as non-biting midges.
Risks & Benefits
They do not bite or sting and pose no direct risk to humans. They are beneficial as a vital food source for fish and birds, and they help recycle nutrients in aquatic habitats. Occasionally, large hatches of adult midges can be a nuisance.
Identified on: 12/31/2025