Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera (true bugs), Cimicidae
Size: Adults typically 4-5 mm (0.16-0.20 inches) long, similar in size to an apple seed.
Natural Habitat
Primarily human dwellings (beds, mattresses, furniture, cracks in walls, etc.), but can be found in any place where humans rest, such as hotels, dorms, and public transportation.
Diet & Feeding
Exclusively feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals, with a strong preference for human blood.
Behavior Patterns
Nocturnal feeders, emerging from hiding spots to feed on sleeping hosts. They are highly resilient and can survive for several months without feeding. Females lay small, white, oval eggs in secluded locations.
Risks & Benefits
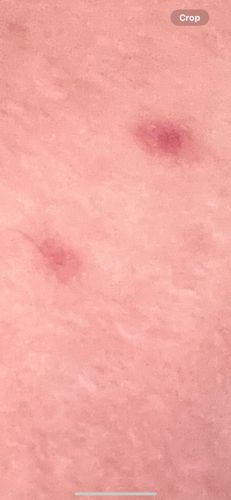
Risks: Bed bug bites can cause itchy welts, leading to discomfort, skin irritation, and potential secondary skin infections from scratching. They are not known to transmit diseases to humans. Benefits: None for humans; they are generally considered pests due to their parasitic nature.
Identified on: 9/6/2025