Human Botfly (or other botfly larvae bite)
Scientific Name: Dermatobia hominis (for human botfly, other species exist for different hosts)
Order & Family: Diptera, Oestridae
Size: Larvae can grow up to 15-20 mm in length.
Natural Habitat
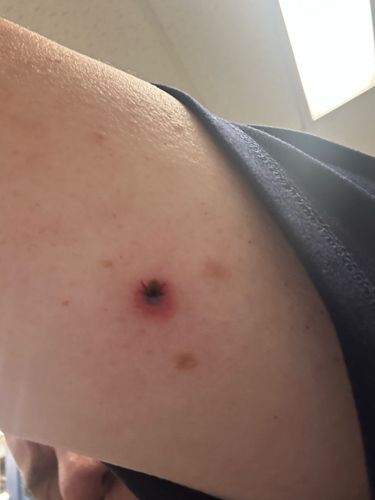
The adult flies live in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas. The larvae develop within the skin of mammals, including humans.
Diet & Feeding
Larvae feed on host tissues and bodily fluids while developing under the skin.
Behavior Patterns
Adult female botflies typically lay their eggs on other arthropods (like mosquitoes or other flies) which then transfer the eggs to a mammalian host. The eggs hatch upon contact with the host's skin (often triggered by body heat), and the larva burrows into the skin, creating a warble (a boil-like lesion with a central breathing hole). The larva develops for several weeks before exiting the host to pupate in the soil.
Risks & Benefits
Risks include discomfort, pain, secondary bacterial infections, potential allergic reactions, and scarring. While generally not life-threatening, if the larva develops in sensitive areas (e.g., around the eyes or brain), it can cause more serious complications. There are no known benefits to humans or the ecosystem from botfly larvae infestation, though parasitic relationships are natural parts of ecosystems.
Identified on: 10/28/2025