Tunga penetrans (Chigoe flea)
Scientific Name: Tunga penetrans
Order & Family: Siphonaptera, Tungidae
Size: Approximately 1 mm (unfed/males) to 10 mm (gravid females in tissue).
Natural Habitat
Sandy, dry soil and dust in tropical and subtropical regions; often found around pigsties and human dwellings in poverty-stricken areas.
Diet & Feeding
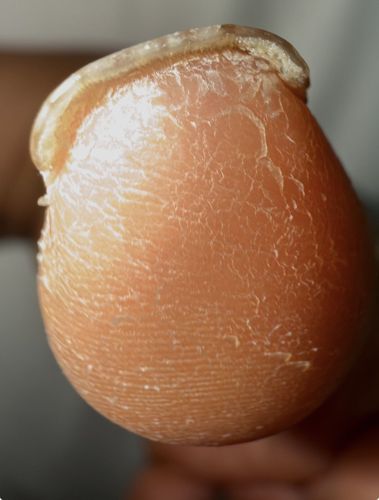
Males and non-breeding females feed on mammal blood (humans, pigs, dogs). Mated females burrow into the host's skin to feed constantly on blood and tissue fluids to produce eggs.
Behavior Patterns
The mated female burrows into the epidermis (specifically the stratum corneum), usually on the feet. Once embedded, it swells significantly (neosome) as its abdomen fills with eggs, which are eventually released through a small opening in the skin.
Risks & Benefits
Causes Tungiasis, characterized by inflammation, severe pain, and itching. Risks include secondary bacterial infections like tetanus, gangrene, and septicemia. There are no ecological benefits to humans; they are considered a significant public health nuisance.
Identified on: 2/4/2026