Human Itch Mite
Scientific Name: Sarcoptes scabiei
Order & Family: Order: Sarcoptiformes, Family: Sarcoptidae
Size: 0.3 to 0.45 millimeters (microscopic)
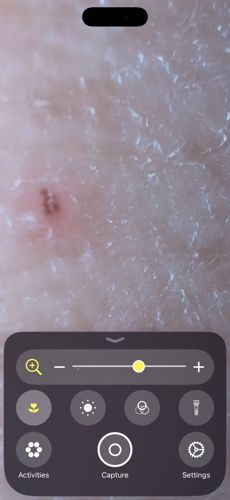
Natural Habitat
Burrows under the surface of human skin, most commonly in folds and crevices between fingers and joints.
Diet & Feeding
Feed on human skin cells and extracellular fluid.
Behavior Patterns
Microscopic mites that burrow into the upper layer of the skin to live and deposit eggs, causing an allergic reaction known as scabies. They are highly contagious and spread through direct skin-to-skin contact.
Risks & Benefits
Cause intense itching and skin rashes (scabies). If left untreated, the itching can lead to secondary skin infections from scratching. They have no ecological benefits and are considered a human parasite.
Identified on: 1/14/2026