Scabies Mite
Scientific Name: Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis
Order & Family: Order: Sarcoptiformes, Family: Sarcoptidae
Size: Microscopic; adult females are approximately 0.30–0.45 mm long and 0.25–0.35 mm wide.
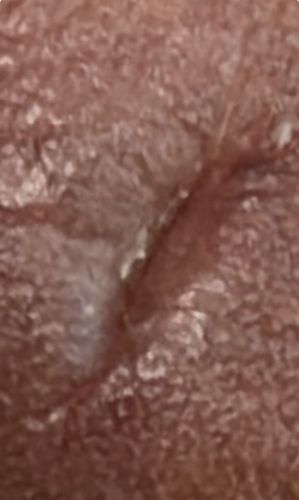
Natural Habitat
The epidermis (upper layer) of human skin, particularly in folds and crevices like between fingers, wrists, armpits, and groin areas.
Diet & Feeding
Feeds on human skin cells and lymph fluid found within the epidermis.
Behavior Patterns
Female mites burrow into the upper layer of the skin to create tunnels where they live, feed, and deposit eggs. This burrowing activity typically intensifies at night.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Causes scabies, a highly contagious skin infestation characterized by intense itching and a pimple-like rash. Scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections like impetigo or staph. There are no ecosystem benefits as it is an obligate parasite.
Identified on: 2/7/2026