Leafminer (general)
Scientific Name: Varies widely (e.g., Liriomyza trifolii, Phyllonorycter blancardella), as 'leafminer' refers to a feeding strategy rather than a single species. Cannot specify without more information.
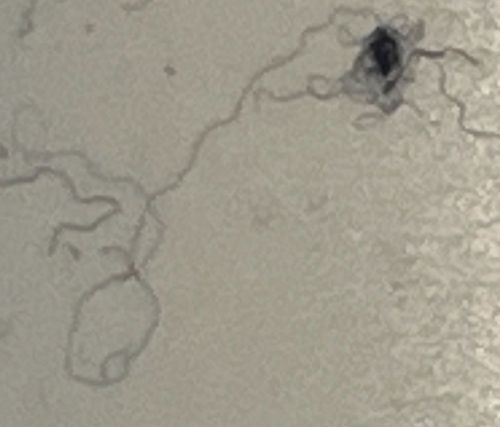
Order & Family: Order: Diptera (flies), Hymenoptera (wasps), Coleoptera (beetles), or Lepidoptera (moths). Family varies widely depending on the specific species (e.g., Agromyzidae for dipteran leafminers, Gracillariidae for lepidopteran leafminers). The image suggests patterns typical of insect larvae burrowing within a surface.
Size: Larvae are typically very small, a few millimeters in length, as they live within leaf tissue. Adult insects vary depending on the specific group: flies (1-5 mm), moths (2-15 mm wingspan), beetles (1-10 mm), wasps (1-5 mm).
Natural Habitat
Found on a wide variety of plants, including agricultural crops, ornamental plants, and wild flora, wherever their host plants grow.
Diet & Feeding
Larvae feed on sap and plant tissue within leaves. Adults may feed on nectar or pollen, or not feed at all.
Behavior Patterns
Larvae tunnel within the epidermal layer of leaves, creating serpentine mines. The specific pattern of the mine can often help identify the species. Adults are free-flying and lay eggs on plant surfaces.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include significant damage to agricultural crops and ornamental plants, leading to reduced yields and aesthetic damage. Benefits are generally limited, though some species may contribute to natural plant pruning in wild settings. Some parasitic wasps that prey on leafminers are beneficial for biological control.
Identified on: 9/2/2025