Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera (order), Cimicidae (family)
Size: Adults are typically 4-5 mm (0.16-0.20 inches) long, similar to an apple seed. Nymphs are smaller and translucent.
Natural Habitat
Primarily found in human dwellings, especially in bedrooms. They hide in mattresses, bed frames, headboards, cracks in walls, furniture, and behind wallpaper. They are highly adaptable and can be found almost anywhere people rest.
Diet & Feeding
Exclusively hematophagous, meaning they feed solely on the blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily humans.
Behavior Patterns
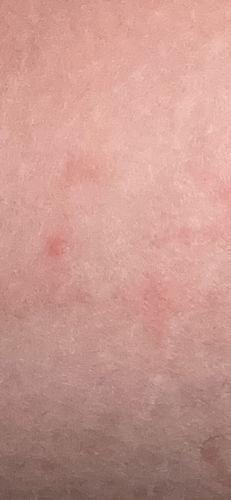
Bed bugs are nocturnal and feed on blood while their hosts are asleep. They are very adept at hiding in cracks and crevices during the day, making them difficult to detect. Bites often appear in lines or clusters.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Bed bug bites can cause itchy welts, skin irritation, and in some cases, secondary skin infections from scratching. They do not transmit diseases. Benefits: None to humans; in nature, they could be considered part of the food web for other insects, but they are generally considered pests.
Identified on: 9/4/2025