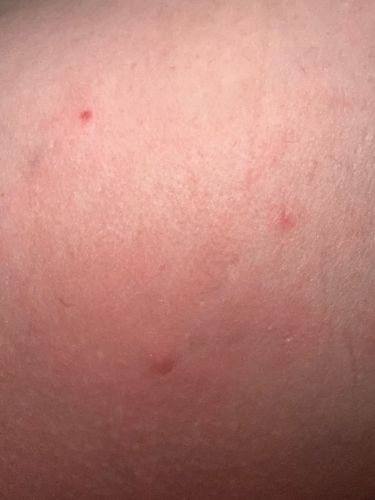
Mosquito (bite marks)
Scientific Name: Various genera within Culicidae (e.g., Aedes, Anopheles, Culex)
Order & Family: Order: Diptera, Family: Culicidae
Size: Adult mosquitoes typically range from 3 to 10 mm (0.12 to 0.39 inches) in length.
Natural Habitat
Mosquitoes are found globally in a wide range of habitats, particularly in areas with standing water, which is essential for their larval and pupal stages. This includes ponds, swamps, marshes, ditches, and even small containers of water around human dwellings.
Diet & Feeding
Female mosquitoes feed on blood (from humans and animals) for reproduction. Both male and female mosquitoes feed on nectar, plant sap, and other sugary substances for energy.
Behavior Patterns
Mosquitoes are most active during dawn and dusk but can bite at any time of day. Only female mosquitoes bite, as they require a blood meal for egg development. They are attracted to carbon dioxide, body heat, and certain chemicals present on human skin. After feeding, females rest to digest the blood meal and then lay eggs in water.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include transmitting diseases such as West Nile virus, Zika virus, dengue fever, malaria, chikungunya, and filariasis. Mosquito bites can also cause intensely itchy welts due to allergic reactions to their saliva. Benefits are minimal to humans, but mosquitoes serve as a food source for other animals (e.g., birds, bats, fish) and play a role in pollination for some plants.
Identified on: 9/4/2025