Mosquito
Scientific Name: Various genera within Culicidae (e.g., Aedes, Anopheles, Culex)
Order & Family: Order: Diptera, Family: Culicidae
Size: 3-6 mm (0.12-0.24 inches)
Natural Habitat
Mosquitoes are found globally, thriving in warm, humid environments. They require standing water for breeding, which can include puddles, swamps, containers, and even small amounts of water in objects like tires or gutters.
Diet & Feeding
Female mosquitoes consume blood from a variety of hosts (mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians). Both male and female mosquitoes feed on nectar and plant juices for energy.
Behavior Patterns
Mosquitoes are most active during dawn and dusk but can bite at any time. Females require a blood meal to produce eggs, which are laid in standing water. Males feed on nectar. Their flight is characterized by a distinctive high-pitched buzzing sound.
Risks & Benefits
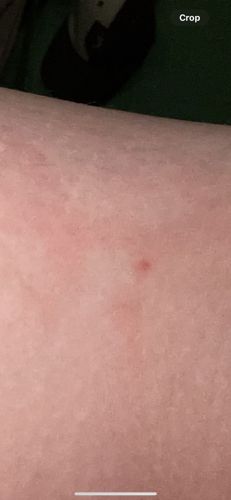
Risks: Mosquitoes are significant vectors for numerous diseases including malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, West Nile virus, and chikungunya. Their bites cause itchy welts. Benefits: In their larval stage, they can be a food source for aquatic animals. Adult mosquitoes can serve as pollinators for some plants, though this role is minor compared to their disease-carrying capacity.
Identified on: 9/4/2025