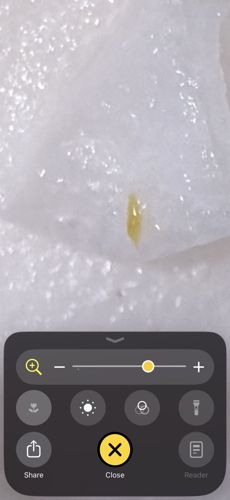
Pinworm (Egg/Nits phase)
Scientific Name: Enterobius vermicularis
Order & Family: Order: Oxyurida, Family: Oxyuridae
Size: Eggs are roughly 50 to 60 micrometers; adult females are 8 to 13 millimeters.
Natural Habitat
The human large intestine; eggs are often found on perianal skin, clothing, and bedding.
Diet & Feeding
They feed on host nutrients and intestinal contents within the human digestive tract.
Behavior Patterns
Adult females migrate to the anus at night to deposit eggs, causing intense itching. This leads to scratching and the transfer of eggs to hands and surfaces.
Risks & Benefits
Risks include enterobiasis (pinworm infection), itching, and disturbed sleep. There are no known ecological benefits to human health.
Identified on: 1/14/2026