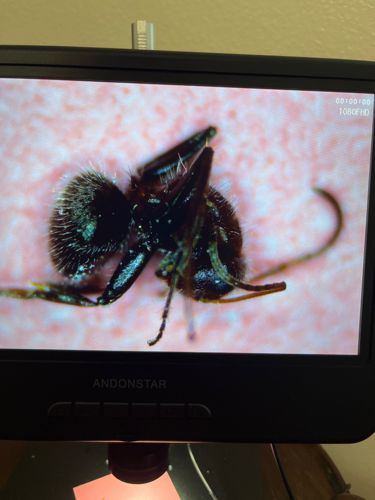
Ant
Scientific Name: Formicidae (family)
Order & Family: Hymenoptera (Order), Formicidae (Family)
Size: Generally, ants range from 1 mm to 30 mm (0.04 to 1.2 inches) in length, depending on the species and caste.
Natural Habitat
Ants are found in almost all terrestrial habitats around the world, from forests and grasslands to deserts and urban environments. They typically live in colonies underground, in mounds, or within wood.
Diet & Feeding
Ants are omnivores with a diverse diet. They feed on nectar, seeds, fungi, other insects (both living and dead), and honeydew produced by aphids. The specific diet varies by species.
Behavior Patterns
Ants are highly social insects living in organized colonies with a queen, workers, and males. Workers forage for food, care for the young, and defend the nest. They communicate through chemical signals (pheromones) and tactile interactions. Many species exhibit elaborate nest-building behaviors.
Risks & Benefits
Risks include potential stings (some species, like fire ants, have painful stings), property damage (e.g., carpenter ants nesting in wood, pavement ants undermining structures), and contamination of food. Benefits include pest control (preying on other insects), soil aeration and nutrient cycling, and seed dispersal for plants.
Identified on: 10/22/2025