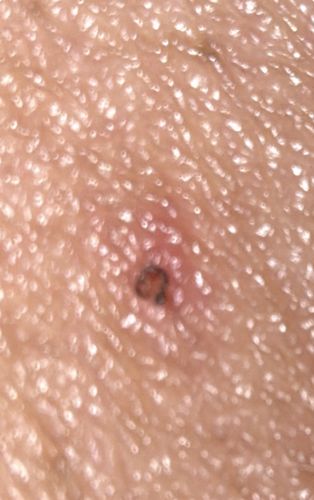
Tick (likely a Nymph or Seed Tick)
Scientific Name: Ixodida (Order)
Order & Family: Order: Ixodida; Families: Ixodidae (hard ticks) or Argasidae (soft ticks)
Size: Varies significantly by life stage; Larvae are <1mm (poppy seed size), Nymphs are 1-2mm, and Adults can range from 3-5mm (unfed) to upwards of 10mm when engorged.
Natural Habitat
Found worldwide, primarily in moist, humid environments such as woody or grassy areas, leaf litter, and shrubs where they can wait for hosts.
Diet & Feeding
Hematophagous (blood-feeding); they parasitize mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians.
Behavior Patterns
Ticks undergo four life stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. They exhibit 'questing' behavior, waiting on the tips of vegetation with front legs extended to latch onto passing hosts. They burrow their mouthparts into skin to feed for several days.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Ticks are significant vectors for disease. They can transmit Lyme disease (Borrelia burgdorferi), Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Ehrlichiosis, and Babesiosis to humans and pets. Benefits: They serve as a food source for birds, reptiles, and amphibians, though they are largely considered pests.
Identified on: 2/17/2026