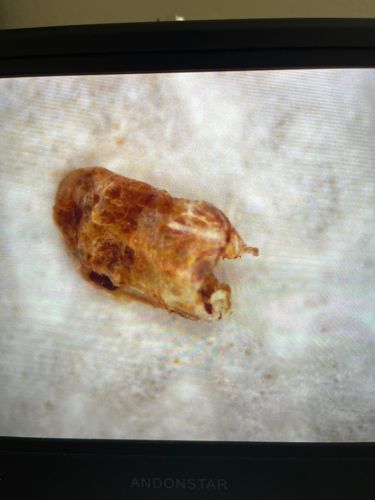
It is difficult to definitively identify the common name of the object in the image. Although it appears to be an exuvia (molted exoskeleton) of an insect, or possibly a dried up insect remains, its exact common name cannot be determined without clearer details or a more complete specimen.
Scientific Name: Based on the image, a precise scientific name cannot be provided. The object appears to be insect remnants or an exuvia. Without features allowing identification to a specific class, order, family, genus, or species, no scientific name can be reliably assigned.
Order & Family: The image shows what appears to be an arthropod exuvia or dried remains. Due to the lack of clear morphological features, it's impossible to determine the taxonomic order and family. The object has a general insect-like shape, but crucial details for classification are missing.
Size: Given the image, it is impossible to determine the actual size of the object as there is no scale provided. Assuming it is an insect exuvia, it could range from a few millimeters to several centimeters depending on the insect species.
Natural Habitat
As the object is likely an exuvia or dried insect remains, its original habitat would depend on the specific species it came from. Generally, insect habitats are diverse, ranging from terrestrial environments like forests, grasslands, and deserts, to aquatic systems including ponds, rivers, and even urban settings. The background in the image appears to be a light-colored, possibly textile or paper surface, which isn't indicative of a natural habitat.
Diet & Feeding
Since the object is not a living organism but rather an exuvia or dried remains, it does not have a diet. The diet would be characteristic of the living insect it once belonged to. Insect diets are highly varied, including herbivores (feeding on plants), carnivores (feeding on other insects or small animals), detritivores (feeding on decaying matter), and omnivores.
Behavior Patterns
As the object is not a living insect, it exhibits no behavior patterns. If it is an exuvia, it represents the shed skin left behind after an insect molts as it grows. Molting is a physiological process in which an arthropod sheds its cuticle (exoskeleton), which is then replaced by a new, larger one. This process is essential for growth.
Risks & Benefits
As an inanimate object (exuvia or dried remains), there are no inherent risks or benefits associated with the object itself. If it were a living insect, potential risks or benefits would depend entirely on the species. Many insects are beneficial (e.g., pollinators, decomposers, pest controllers), while some can be pests, disease vectors, or cause allergic reactions.
Identified on: 11/11/2025