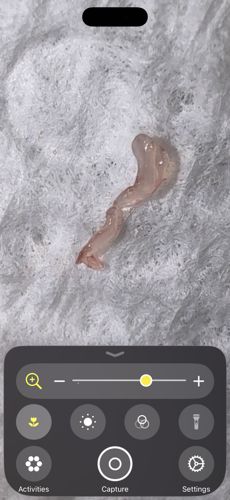
Earthworm (Juvenile or fragmented)
Scientific Name: Lumbricina (Suborder)
Order & Family: Order: Opisthopora; Family: Lumbricidae
Size: 1 cm to over 30 cm depending on species and age.
Natural Habitat
Moist soil, leaf litter, and compost rich in organic matter.
Diet & Feeding
Decomposing organic matter, including decaying leaves, soil, and microscopic organisms.
Behavior Patterns
Fossilial; they burrow through soil, emerging primarily at night or during heavy rains to avoid desiccation. They are hermaphroditic and play a key role in soil aeration.
Risks & Benefits
Highly beneficial to the ecosystem as they improve soil fertility and structure. They pose no risk to humans, though some species can be invasive in forests where they accelerate leaf litter decomposition.
Identified on: 12/26/2025