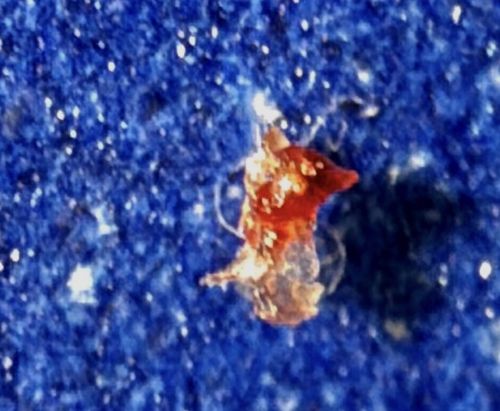
Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Order: Hemiptera, Family: Cimicidae
Size: Adults are approximately 4–5 mm long (about the size of an apple seed) and 1.5–3 mm wide. Nymphs (juveniles) are smaller, ranging from 1 mm to 4 mm.
Natural Habitat
Typically found indoors in close proximity to human sleeping areas. They hide in cracks and crevices of beds, mattresses, box springs, headboards, and furniture frames, as well as behind baseboards and wallpaper.
Diet & Feeding
Hematophagous, meaning they feed exclusively on the blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily humans. They prefer to feed at night while their host is sleeping.
Behavior Patterns
They are nocturnal and elusive, hiding during the day in tight spaces. They do not fly or jump but crawl quickly. Their life cycle includes egg, five nymphal stages (each requiring a blood meal to molt), and adult.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Bed bugs are considered a major nuisance pest. Their bites can cause itchy red welts, allergic reactions, and secondary skin infections from scratching. They can cause significant psychological distress, anxiety, and insomnia. They are not known to transmit diseases to humans. Benefits: None known in a domestic context.
Identified on: 2/10/2026