Ant
Scientific Name: Formicidae
Order & Family: Hymenoptera, Formicidae
Size: Most ants range from 2 to 7 millimeters (0.08 to 0.28 inches) in length, though some larger species can exceed 2.5 cm (1 inch).
Natural Habitat
Ants are found almost everywhere on Earth, except Antarctica and a few remote islands. They inhabit a wide range of environments including forests, deserts, grasslands, urban areas, and even within homes.
Diet & Feeding
Ants are opportunistic feeders, with diets varying by species. They can be herbivores, predators, scavengers, or omnivores. Common food sources include nectar, seeds, fungi, other insects, and household food scraps.
Behavior Patterns
Ants are highly social insects that live in structured colonies. They exhibit complex behaviors such as division of labor (queens, males, workers), communication through pheromones, nest building, and foraging for food. Many species demonstrate cooperative care of the young and defensive behaviors.
Risks & Benefits
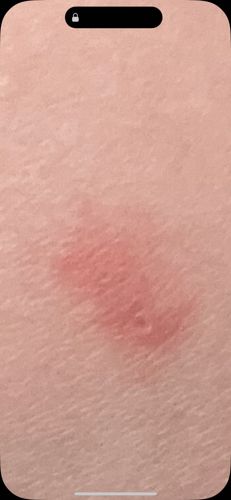
Risks include potential for painful stings or bites from some species (e.g., fire ants), which can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Some species can also be considered pests when they infest homes or gardens. Benefits include roles as natural pest controllers (preying on other insects), soil aerators, and seed dispersers, contributing to ecosystem health.
Identified on: 9/7/2025