Louse egg (Nit)
Scientific Name: Pediculus humanus capitis (for head louse)
Order & Family: Phthiraptera, Pediculidae
Size: Approximately 0.8 mm long and 0.3 mm wide
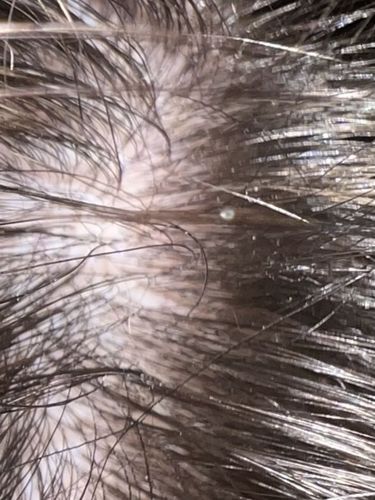
Natural Habitat
Human hair, typically close to the scalp for warmth and moisture
Diet & Feeding
Lice, which hatch from these eggs, feed exclusively on human blood
Behavior Patterns
Nits are laid by female head lice and firmly glued to individual hair shafts. They are usually found within 1 cm of the scalp. They hatch after about 7-10 days, leaving behind a white, empty shell.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Head lice infestations (pediculosis) can cause intense itching, scalp irritation, and secondary bacterial infections due to scratching. They do not transmit diseases. Benefits: None for humans; they are considered a pest.
Identified on: 10/31/2025