Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera / Cimicidae
Size: Adult bed bugs are typically 4-5 mm (0.16-0.20 inches) long, similar in size to an apple seed. Nymphs are smaller and translucent.
Natural Habitat
Bed bugs are typically found in human dwellings, particularly in bedrooms. They hide in mattresses, bed frames, box springs, headboards, furniture, cracks in walls, electrical outlets, and behind baseboards. They can be found in homes, apartments, hotels, dormitories, and even public transportation.
Diet & Feeding
Bed bugs are hematophagous, meaning they feed exclusively on blood. Their primary host is human blood, but they will also feed on pets and other warm-blooded animals.
Behavior Patterns
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal, feeding on humans (or other warm-blooded animals) during their sleep. They are attracted to body heat and carbon dioxide. They tend to hide in cracks and crevices during the day, such as mattress seams, bed frames, furniture, or walls. Females lay several eggs per day, which hatch in 6-17 days, and nymphs mature in about a month under ideal conditions. They can survive for several months without feeding.
Risks & Benefits
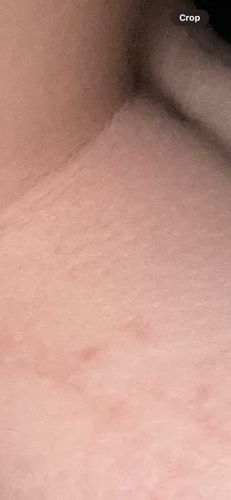
Potential risks include itchy red welts from bites, allergic reactions in some individuals, and secondary skin infections from scratching. They are not known to transmit diseases to humans. There are no known benefits of bed bugs to humans or the ecosystem; they are considered a nuisance pest.
Identified on: 9/4/2025