Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera, Cimicidae
Size: Adults are typically 4-5 mm (about 3/16 inch) in length. Nymphs are smaller.
Natural Habitat
Primarily human dwellings, especially beds, mattresses, bed frames, and cracks in walls. They prefer dark, hidden places close to where hosts sleep.
Diet & Feeding
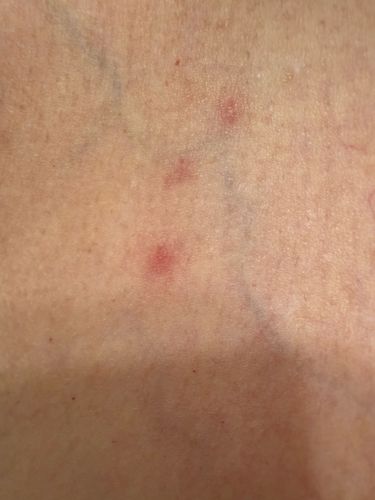
Exclusively blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily humans. They feed by piercing the skin with their elongated mouthparts and sucking blood.
Behavior Patterns
Nocturnal activity, feeding mainly at night while hosts are sleeping. They are attracted to CO2 and body heat. Bed bugs are wingless and cannot fly or jump, but can crawl quickly. They aggregate in harborages and can live for several months without a blood meal.
Risks & Benefits
Potential Risks: Bed bug bites can cause itchy red welts on the skin, leading to discomfort and sleep deprivation. While not known to transmit diseases, heavy infestations can cause psychological distress, anxiety, and even secondary skin infections from scratching. Potential Benefits: No known direct ecological benefits as they are parasites of humans and animals.
Identified on: 9/6/2025