Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera (true bugs), Cimicidae
Size: 4-5 mm (adults), nymphs are smaller
Natural Habitat
Primarily human dwellings, especially bedrooms; they hide in cracks and crevices such as mattress seams, bed frames, furniture, behind wallpaper, and in electrical outlets.
Diet & Feeding
Exclusively blood of warm-blooded animals, preferring human blood. They feed by piercing the skin and drawing blood.
Behavior Patterns
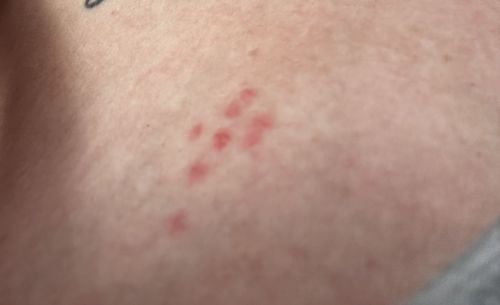
Nocturnal feeders, primarily active at night when hosts are asleep. They are very adept at hiding and can go for extended periods (months) without feeding. Bites often appear in lines or clusters (commonly referred to as 'breakfast, lunch, and dinner').
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include itchy bites leading to skin irritation, allergic reactions, secondary skin infections from scratching, and psychological distress (anxiety, insomnia). They are not known to transmit diseases to humans. There are no known benefits.
Identified on: 9/22/2025