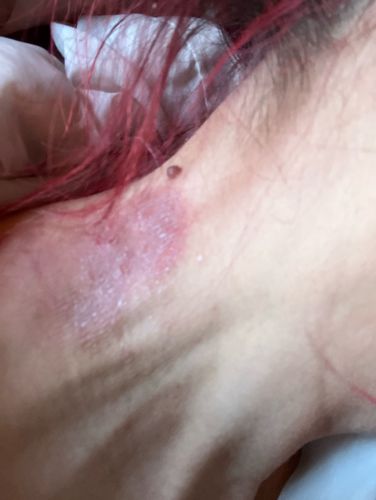
Hard tick
Scientific Name: Ixodidae (Family)
Order & Family: Order: Ixodida; Family: Ixodidae
Size: 1 mm to 5 mm (unfed), but can grow significantly larger (up to 10-15 mm) when fully engorged with blood.
Natural Habitat
Grassy or wooded areas, shrubs, leaf litter, and fields, often found waiting on the tips of vegetation to latch onto a host.
Diet & Feeding
Hematophagous; they feed exclusively on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles/amphibians.
Behavior Patterns
They exhibit 'questing' behavior by climbing vegetation and extending their front legs to latch onto passing hosts. They are slow feeders, remaining attached for several days to complete a blood meal through various life stages (larva, nymph, adult).
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Ticks are major vectors for various pathogens, including the bacteria that cause Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and several other illnesses. They can cause skin irritation, allergic reactions, and localized infections at the bite site. Benefits: They serve as a food source for some reptiles, birds, and amphibians, and act as a natural population control for some wild animal species.
Identified on: 1/13/2026