Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera (Order); Cimicidae (Family)
Size: Adults are typically 4-5 mm (about 3/16 inch) in length.
Natural Habitat
Bed bugs typically live in close proximity to their hosts. They are most commonly found in mattresses, bed frames, box springs, headboards, and other furniture near sleeping areas. They can also hide in cracks and crevices in walls, behind wallpaper, in electrical outlets, and in clutter.
Diet & Feeding
Strictly hematophagous, meaning they feed exclusively on the blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily humans.
Behavior Patterns
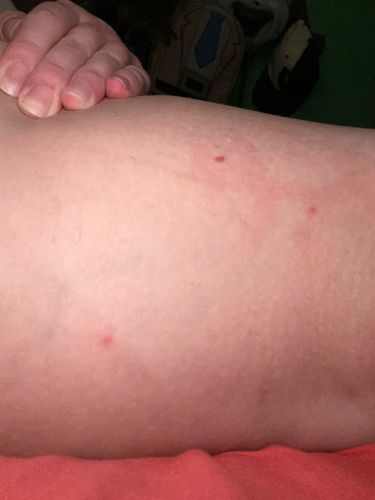
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal, feeding on humans (or other warm-blooded animals) while they sleep. They are attracted to body heat and carbon dioxide. Bites often occur in lines or clusters, sometimes referred to as 'breakfast, lunch, and dinner' patterns.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include itchy red welts (the bites themselves), allergic reactions ranging from mild to severe, and secondary skin infections from scratching. They are not known to transmit diseases to humans. There are no known direct benefits of bed bugs to humans or the ecosystem.
Identified on: 9/4/2025