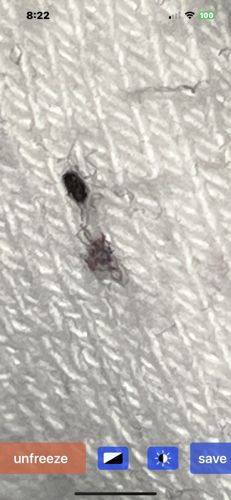
Head louse
Scientific Name: Pediculus humanus capitis
Order & Family: Phthiraptera (Order: Parasitic Lice), Pediculidae (Family)
Size: Adults are typically 2-4 mm long. Nits (eggs) are much smaller, around 0.8 mm.
Natural Habitat
Exclusively on the human scalp, especially behind the ears and near the nape of the neck. Nits are cemented to individual hair shafts.
Diet & Feeding
Human blood, which they feed on several times a day. Their feeding can cause itching.
Behavior Patterns
Head lice spend their entire lives on the human scalp, attaching their eggs (nits) to hair shafts. They crawl, but cannot fly or jump. They are primarily active during the day and can spread through head-to-head contact or sharing personal items.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include intense itching, skin irritation, and secondary bacterial infections from scratching. They do not transmit diseases. There are no known benefits to humans.
Identified on: 8/29/2025