Mosquito
Scientific Name: Culicidae
Order & Family: Diptera, Culicidae
Size: Typically 3 to 9 mm (0.1 to 0.4 inches) in length.
Natural Habitat
Mosquitoes are found globally, predominantly in warm, humid regions. They thrive in areas with standing water, which is essential for larval development. This includes marshes, swamps, ditches, containers holding water, and even puddles.
Diet & Feeding
Adult female mosquitoes feed on blood, which is necessary for egg production. They feed on various animals, including humans, birds, and mammals. Both male and female mosquitoes also feed on nectar and plant juices for energy.
Behavior Patterns
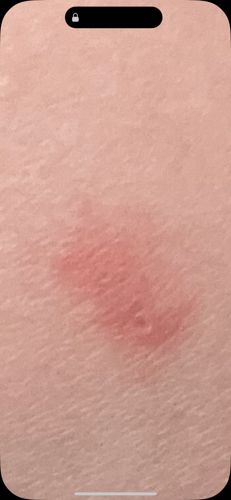
Mosquitoes are most active during dawn and dusk, though some species are active during the day. They locate hosts primarily through detecting carbon dioxide, body heat, and certain chemicals on the skin. The bite reaction, as seen in the image, is caused by the mosquito's saliva, which contains anticoagulants and proteins that can cause an allergic response in humans.
Risks & Benefits
Mosquitoes are significant vectors of diseases, including malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, West Nile virus, and chikungunya. The primary risk to humans is the transmission of these pathogens, leading to illness and sometimes death. Benefits include serving as food for various animals in ecosystems, such as birds, bats, and fish, and in their adult form, some species can act as pollinators for certain plants, although their role as pollinators is generally considered minor compared to other insects.
Identified on: 9/7/2025