Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera (Order), Cimicidae (Family)
Size: Adults are typically 4-5 mm (0.16-0.20 inches) long, unfed; they become larger and engorged after feeding.
Natural Habitat
Bed bugs are typically found in human dwellings, preferring warm environments and close proximity to their hosts. They infest mattresses, box springs, bed frames, furniture, cracks in walls, and other hidden spots within bedrooms.
Diet & Feeding
Strictly hematophagous, meaning they feed exclusively on the blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily humans.
Behavior Patterns
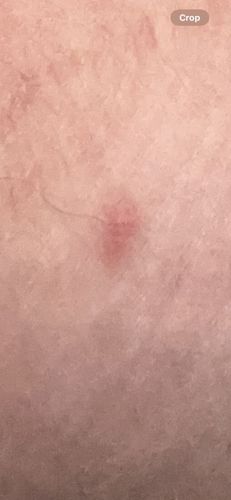
As parasites, bed bugs are primarily active at night, feeding on sleeping hosts. They are highly adept at hiding in crevices and cracks near human sleeping areas, emerging only for blood meals. Their presence can be identified by bites, fecal spots on bedding, and a distinctive sweet, musty odor.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include itchy bites, allergic reactions, secondary skin infections from scratching, and psychological distress from infestations. They are not known to transmit diseases to humans. There are no known benefits of bed bugs to humans or the ecosystem.
Identified on: 9/4/2025