Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera, Cimicidae
Size: Adults are typically 4-5 mm (0.16-0.20 inches) long, about the size of an apple seed. Nymphs are smaller and translucent.
Natural Habitat
Bed bugs are found worldwide. They typically infest dwellings, hiding in mattresses, box springs, bed frames, headboards, cracks in walls, furniture, and luggage. They prefer dark, secluded areas close to their hosts.
Diet & Feeding
Bed bugs are obligate hematophagous parasites, meaning they feed exclusively on the blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily humans.
Behavior Patterns
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal, hiding in cracks and crevices during the day and emerging at night to feed. They are attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide emitted by sleeping hosts. Females can lay hundreds of eggs over a lifetime. Nymphs (immature bed bugs) molt five times before reaching maturity, requiring a blood meal between each molt.
Risks & Benefits
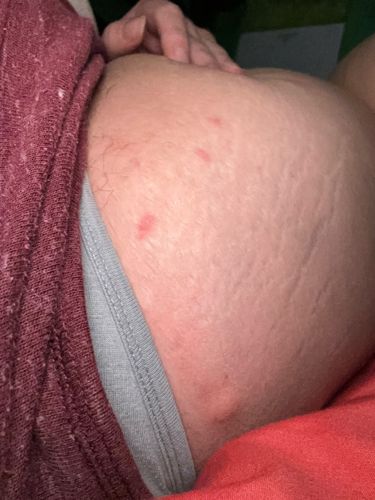
Risks: Bed bug bites can cause itchy welts, leading to skin irritation, allergic reactions, and secondary skin infections from scratching. While not known to transmit diseases, their presence can cause significant psychological distress, anxiety, and sleep deprivation. Benefits: None known to humans; they are generally considered pests.
Identified on: 9/4/2025