Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera (order), Cimicidae (family)
Size: Adult bed bugs are usually 4 to 5 mm (0.16 to 0.20 inches) long.
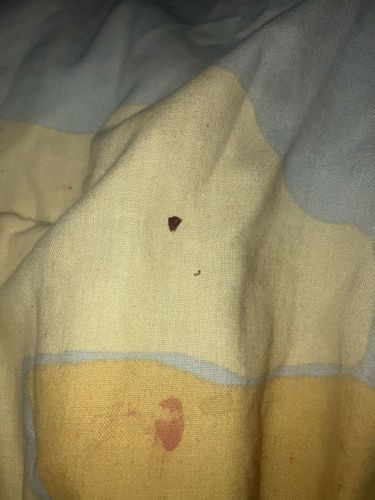
Natural Habitat
Bed bugs are typically found in human dwellings, particularly in beds, mattresses, bed frames, cracks in walls, furniture, and other dark, secluded areas close to their human hosts. They are most active at night.
Diet & Feeding
Bed bugs are obligate hematophagous insects, meaning they feed exclusively on the blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily humans. They pierce the skin with a stylet fascicle and feed on blood.
Behavior Patterns
Nocturnal feeders, bed bugs hide during the day and emerge at night to feed. They are attracted to carbon dioxide and body heat. Females lay eggs individually in secluded spots, and nymphs undergo five molts, requiring a blood meal at each stage to develop.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include itchy red welts from bites, allergic reactions (in some individuals), secondary skin infections from scratching, and psychological distress from infestations. They are not known to transmit diseases to humans. There are no known benefits.
Identified on: 10/7/2025