Ant
Scientific Name: Formicidae
Order & Family: Hymenoptera, Formicidae
Size: Typically 2 to 25 mm (0.08 to 1 inch), depending on the species.
Natural Habitat
Ants are found almost everywhere on Earth, except Antarctica and a few remote islands. They build nests in a wide variety of places including underground, in wood, under rocks, or within household structures.
Diet & Feeding
Ants have diverse diets. Many are omnivores, feeding on nectar, seeds, fungi, other insects (both living and dead), and household food scraps. Some species specialize, for example, on honeydew produced by aphids or cultivating fungi.
Behavior Patterns
Ants are highly social insects living in colonies that can range from a few dozen to millions of individuals. Colonies typically consist of one or more queens, many sterile female workers, and male drones. They communicate through pheromones, engage in complex foraging, nest-building, and defensive behaviors, and have a caste system.
Risks & Benefits
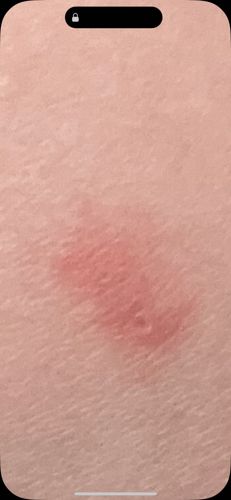
Risks: Some ant species can bite or sting, causing pain, itching, and in rare cases, allergic reactions. They can also become household pests, contaminating food or damaging property (e.g., carpenter ants). Benefits: Ants play crucial roles in ecosystems as decomposers, aerating soil, dispersing seeds, and preying on other insects, which can help control pest populations.
Identified on: 9/7/2025