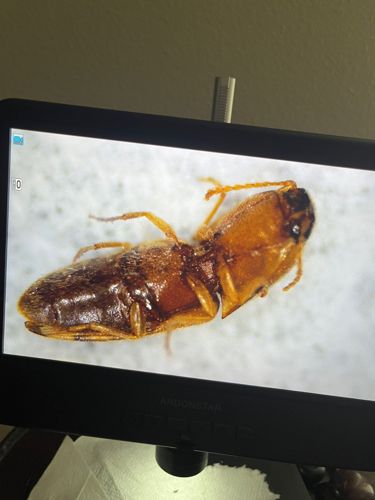
Click Beetle (Wireworm for larvae)
Scientific Name: Family Elateridae
Order & Family: Order Coleoptera, Family Elateridae
Size: Typically 0.2 to 2 inches (5-50 mm) long.
Natural Habitat
Adult click beetles are often found in gardens, fields, and forests, on plants or under bark. Larvae (wireworms) live in soil and rotting wood.
Diet & Feeding
Adult click beetles generally feed on pollen, nectar, or plant sap, but some are predaceous. Wireworms (larvae) are primarily herbivores, feeding on roots, seeds, and underground stems, and can be significant agricultural pests. Some wireworm species are also predatory on other soil insects.
Behavior Patterns
Adult click beetles are known for their ability to 'click' and flip themselves into the air when overturned, using a special spine and groove mechanism between their prothorax and mesothorax. This is a defense mechanism to escape predators. They are active during the day or night depending on the species. Larvae (wireworms) spend several years in the soil before pupating and emerging as adults.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Wireworms (larvae) can be significant agricultural pests, causing damage to crops like corn, potatoes, and wheat by feeding on roots and seeds, leading to yield loss. Benefits: Adult click beetles are generally harmless to humans and plants. Some species' larvae are predatory on other pest insects in the soil, providing a natural pest control benefit.
Identified on: 10/4/2025