Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera (Order), Cimicidae (Family)
Size: Adults are typically 4-5 mm (0.16-0.20 inches) long, similar to an apple seed. Nymphs (juveniles) are smaller.
Natural Habitat
Primarily indoor environments where humans reside, such as beds, mattresses, bed frames, furniture, cracks in walls, and luggage. They are common in homes, hotels, dormitories, and other shared living spaces.
Diet & Feeding
Strictly hematophagous, meaning they feed exclusively on the blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily humans.
Behavior Patterns
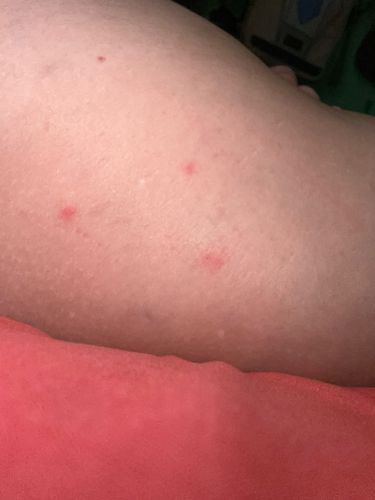
Bed bugs are nocturnal and feed on blood while their hosts (humans or animals) are sleeping. They are attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide. They often bite in lines or clusters, reflecting how they move and feed. They hide in cracks and crevices during the day.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include itchy bites, skin irritation, secondary skin infections from scratching, and psychological distress (anxiety, insomnia). They are not known to transmit diseases to humans. There are no known benefits to humans or the ecosystem.
Identified on: 9/4/2025