Human Itch Mite (Scabies Mite)
Scientific Name: Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis
Order & Family: Sarcoptiformes / Sarcoptidae
Size: Microscopic (Females: 0.30–0.45 mm; Males: 0.20–0.24 mm)
Natural Habitat
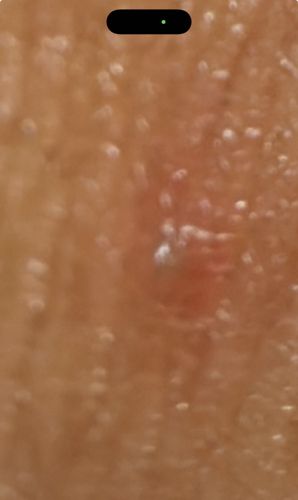
Burrows within the stratum corneum (outer layer) of human skin
Diet & Feeding
Dissolved human skin tissue and cellular fluids
Behavior Patterns
Parasitic; females tunnel into the epidermis to lay eggs, creating characteristic burrow lines or small blister-like bumps (vesicles) on the skin surface. They are typically transferred via prolonged skin-to-skin contact.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: causes Scabies, a condition characterized by intense itching (pruritus) which worsens at night, and a pimple-like skin rash. Scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections.
Identified on: 2/4/2026