Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera, Cimicidae
Size: Adults typically 4-5 mm (0.16-0.20 inches) long, similar to an apple seed.
Natural Habitat
Primarily human dwellings, especially beds, mattresses, and furniture, but also found in cracks and crevices in walls, behind wallpaper, and in electrical outlets.
Diet & Feeding
Exclusively hematophagous, meaning they feed solely on blood. They prefer human blood but will feed on other mammals and birds if humans are unavailable.
Behavior Patterns
Nocturnal feeders, primarily active at night when hosts are sleeping. They are attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide. They tend to live in groups in harborage areas close to their feeding source. Females can lay 1-5 eggs per day, totaling hundreds in their lifetime. Their entire life cycle from egg to adult can take anywhere from 1 to 4 months, depending on temperature and food availability.
Risks & Benefits
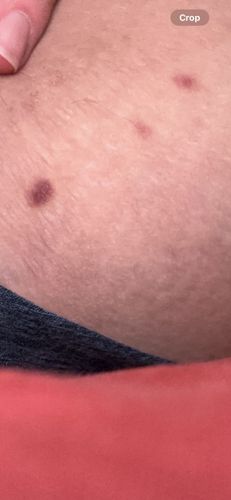
Potential Risks: Bed bug bites can cause itchy welts, skin irritation, and allergic reactions in some individuals. While not known to transmit diseases, heavy infestations can lead to sleep deprivation, stress, and secondary skin infections due to scratching. Potential Benefits: No known direct benefits to humans or the ecosystem; they are considered pests.
Identified on: 9/6/2025