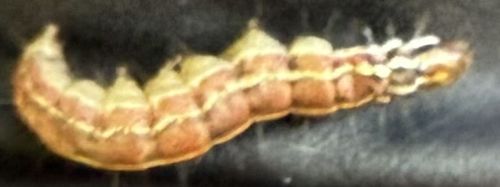
Armyworm (likely Fall Armyworm or a similar species)
Scientific Name: Spodoptera frugiperda (for Fall Armyworm, a common and widespread species with this appearance)
Order & Family: Lepidoptera, Noctuidae
Size: Larvae (caterpillars) typically range from 1 to 1.5 inches (25-38 mm) in length when fully grown.
Natural Habitat
Armyworms thrive in warm, humid climates. They are typically found in agricultural fields, grasslands, pastures, and other areas with abundant host plants. They are migratory pests, able to spread over long distances, often carried by winds.
Diet & Feeding
Armyworms are polyphagous, meaning they feed on a wide variety of plants. They are significant agricultural pests, consuming leaves, stems, and sometimes fruits of crops like corn, wheat, rice, sorghum, pasture grasses, and various vegetables. They can cause severe defoliation, especially during outbreaks.
Behavior Patterns
Armyworms are primarily nocturnal feeders, active at night. During the day, they often hide at the base of plants or in soil cracks. They are known for their 'marching' behavior, especially when food sources in one area are depleted, causing large groups to move to new fields. They undergo complete metamorphosis, with larvae (caterpillars) pupating in the soil before emerging as adult moths.
Risks & Benefits
Potential Risks: Armyworms are major agricultural pests capable of causing significant economic losses by destroying crops. Their rapid reproduction and migratory nature can lead to widespread damage. Potential Benefits: In their natural ecosystems, they can serve as a food source for various predators and parasitoids. However, their pest status far outweighs any ecological benefits in agricultural settings.
Identified on: 8/15/2025