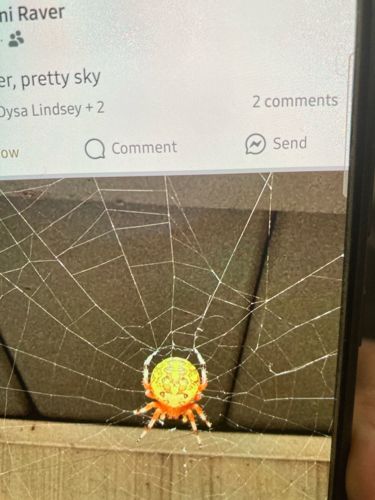
Marbled Orb Weaver
Scientific Name: Araneus marmoreus
Order & Family: Araneae, Araneidae (Orb-weavers)
Size: Females typically range from 9 to 18 mm (0.35 to 0.71 inches); males are smaller, usually 5 to 9 mm (0.20 to 0.35 inches).
Natural Habitat
Often found in wooded areas, gardens, tall grasses, and shrubbery. They prefer to build their large orb webs between trees, shrubs, or structures, often near water or lights that attract insects.
Diet & Feeding
Primarily preys on various flying insects such as flies, moths, beetles, and sometimes larger insects that get entangled in their web.
Behavior Patterns
They are known for constructing large, intricate orb webs, often several feet in diameter, which they build at dusk and often consume or rebuild at dawn. The spider typically rests in the center of the web or in a retreat nearby, waiting for prey. Females are more colorful and robust than males. Mating occurs in late summer to early fall, and females lay eggs in a silk sac before dying with the onset of cold weather.
Risks & Benefits
Potential Risks: Marbled Orb Weavers are not considered dangerous to humans. Their venom is mild, and a bite would typically only result in localized pain, redness, and swelling, similar to a bee sting. They are not aggressive and will only bite if severely provoked or handled roughly. Potential Benefits: They are beneficial to ecosystems by controlling insect populations, particularly agricultural and garden pests. Their webs also serve as a natural indicator of environmental health.
Identified on: 9/28/2025