Bed Bug
Scientific Name: Cimex lectularius
Order & Family: Hemiptera, Cimicidae
Size: Adult bed bugs are typically 4-5 mm long, oval-shaped, and reddish-brown.
Natural Habitat
Bed bugs primarily live in human dwellings, typically in crevices and cracks of mattresses, bed frames, furniture, and walls. They are found worldwide.
Diet & Feeding
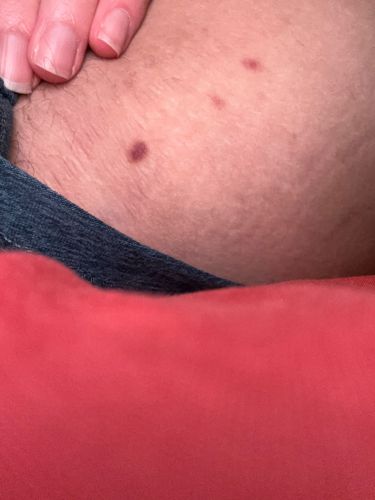
Bed bugs are nocturnal parasites that feed exclusively on the blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily humans. They feed by piercing the skin with their elongated mouthparts and drawing blood.
Behavior Patterns
Bed bugs are elusive and mostly active at night. They hide during the day and emerge to feed, usually taking about 3-10 minutes to engorge with blood. They are attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide. Females lay 1-12 eggs per day, typically for 2-3 months, often in secluded locations.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include itchy red welts from bites, allergic reactions, and secondary skin infections from scratching. They are not known to transmit diseases in humans. There are no known benefits of bed bugs to the ecosystem; they are considered a nuisance pest.
Identified on: 9/6/2025