Itch Mite (Scabies Mite)
Scientific Name: Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis
Order & Family: Order: Sarcoptiformes, Family: Sarcoptidae
Size: Microscopic; females are typically 0.30–0.45 mm long and 0.25–0.35 mm wide, while males are significantly smaller.
Natural Habitat
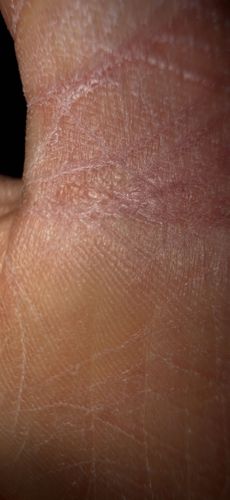
The mite is an obligate parasite that lives exclusively within the epidermis (the top layer of skin) of humans. It cannot survive long away from a host.
Diet & Feeding
They feed on dissolved human tissues and fluids found within the skin layers as they burrow.
Behavior Patterns
The female mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin to lay eggs, creating serpentine tunnels (burrows) often visible as fine, raised lines. This activity triggers an intense allergic reaction and severe itching, especially at night.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Causes scabies, a highly contagious skin infestation characterized by intense itching and a pimple-like rash. Scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections like impetigo or cellulitis. Benefits: None; it is a parasitic pest.
Identified on: 2/9/2026