Flea
Scientific Name: Siphonaptera (order), various species
Order & Family: Order Siphonaptera
Size: 1.5 to 3.3 mm (0.06 to 0.13 inches)
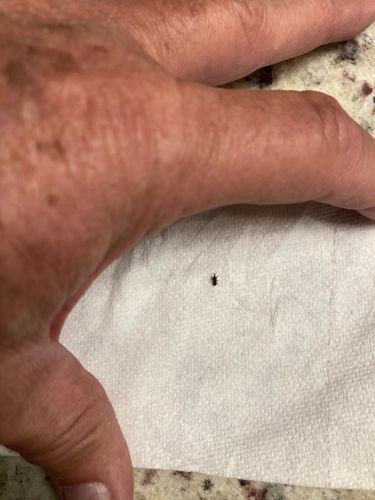
Natural Habitat
Warm-blooded animal hosts (mammals and birds), pet bedding, carpets, cracks in floors, upholstered furniture, shaded outdoor areas
Diet & Feeding
Blood (hematophagous) of mammals and birds. They feed by piercing the skin and sucking blood.
Behavior Patterns
Fleas are wingless insects known for their ability to jump long distances. They undergo complete metamorphosis (egg, larva, pupa, adult). Adults spend most of their lives on the host, while eggs, larvae, and pupae are often found in the environment. They are attracted to warmth, vibrations, and carbon dioxide, which signal the presence of a host.
Risks & Benefits
Potential risks include causing itchy bites, allergic reactions (flea allergy dermatitis), and transmitting diseases such as Bartonellosis (cat scratch disease), Rickettsiosis (murine typhus), and tapeworms (Dipylidium caninum) to pets and sometimes humans. There are no known direct benefits to humans, but they are part of the food chain for other insects and small animals.
Identified on: 9/17/2025